The World Gem Foundation’s ‘Project Africa’ Aims to Level the Playing Field
In a Q&A, founder Geoff Dominy shares WGF’s plans for training a generation of gemologists in gem-producing countries in Africa.

The foundation has 17 gem academies globally, but recently set its sights on leveling the playing field in source countries in Africa by making gemological education accessible and affordable there.
Project Africa just launched its first phase in Ethiopia.
While working on the initiative in the country, World Gem Foundation founder Geoff Dominy recently granted National Jeweler an email interview to learn more about it. Here’s what he had to say.
National Jeweler: When did the idea for Project Africa take form, and why did you want to do it?
Geoff Dominy: I remember visiting the Tucson Gem and Mineral Show in the late 1980s and talking to dealers from Sri Lanka. For many, Tucson was their first experience outside of Sri Lanka and they were amazed at the prices. It was a real eye opener. They finally realized the true value of their goods on the world stage.
When I started the World Gem Foundation in 2015, one of the mandates was to make gemological education accessible and affordable in the key gem-producing areas. Even today, gem producers in certain parts of the world are oblivious to their true value, and while this obviously benefits foreign buyers, the reality is that most gem-producing areas are also the poorest. We need to change the current dynamic. The people living in these gem-rich areas must benefit socially and economically from these valuable resources.
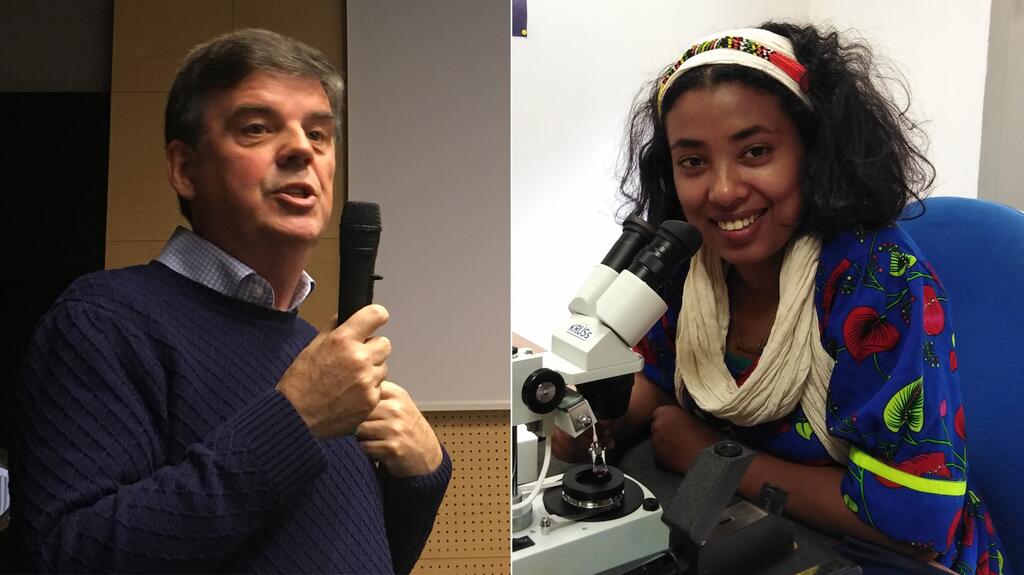

Project Africa really took off in February 2022. One of our Ethiopian scholarship students Haimanot Sisay came to Mallorca, Spain, to complete her practical studies. She talked about her dream of bringing gemological education to Ethiopia and Africa. She was passionate about it. She was looking for an organization to support her and to make courses and programs available. We were completely on the same page, and I promised her that if she could get the ‘powers to be’ to commit to supporting us, we would come to Ethiopia.
For the next eight months, she worked tirelessly, meeting the minister of mines and anyone who might help, including the University of Addis Ababa. Finally, we reached the point where we felt it was necessary for me to come and show that we were fully committed. Moving to Ethiopia made a huge ‘statement of intent’ that really seems to have mobilized the people here. The energy and support I have witnessed over the last five weeks have been amazing. It’s a testament to the fact that if everyone works together anything is possible.
Haimanot is now our director of operations for Project Africa because she deserves to take full credit for getting us this far.
NJ: What exactly is its mission?
GD: It’s to finally give Africans the gemological educational tools they need to responsibly manage their gem resources. With our 1000/10 initiative, we are aiming to train 1,000 gemologists over the next 10 years so we can create a pool of professional gemologists who will ensure Africa benefits from these resources.
NJ: What has been the process to get the initiative going? What challenges did you run into?
GD: One of the biggest challenges in business is to understand the culture, the mentality, and the unique aspects of life. I lived in Spain for eight years, and Starbucks have started opening stores there. They want to Americanize Spanish coffee. Spaniards are very particular about their coffee, and they don’t want foreigners coming in and imposing their ‘style’ of doing business. The same is true here in Ethiopia and Africa. You must be sensitive to the cultural differences. We are guests here, therefore we need to be respectful and find a way of doing business that does not alienate the people here.
At the World Gem Foundation, we talk about training the next generation of gemologists, but here in Africa, there is not even a first generation of gemologists. This must change.
I have never been one to ask for help, so ‘funding’ is completely foreign to me. However, even in five short weeks, I now understand why it is necessary. People simply do not have money, so how do you educate them if they cannot afford it? If we want to reach as many people as possible, we must find a way to fund this program. Nothing in life is for free. Someone somewhere bears the cost. If it is not the end user, then it is somebody else along the food chain. Some things can be provided for free but others, such as teachers’ salaries, are harder to absorb. We are not a huge company, so unlike other organizations, we cannot simply write this off. We are a not-for-profit Canadian company; we are not a registered charity.
So, funding will always be the major challenge. I do believe, however, that the timing is right to start this initiative. I watched in disbelief a video that has gone viral called ‘Keep Africa Poor.’ It talks about the resources here in Africa and their importance to the rest of the world. The problem is the rest of the world does not want to pay fair value for these resources. They want to protect the bottom line. Paying more means charging more and that is not good for business.
Over the last hundred years, billions and billions of dollars of raw materials have been taken out of Africa, and yet Africa is still poor. Everyone I have spoken to here has seen the video and they share my viewpoint. Yes, I understand that all these resources are needed, but how can we take them and leave the host countries impoverished?
NJ: You’ve just begun the first phase. What does that include?
GD: The first phase includes creating a Centre of Excellence that will offer the World Gem Foundation gemological programs. This will be a joint venture with an Ethiopian corporation that shares our vision, and we are hoping to start the first 25-week Career Gemmologist Diploma program (750 hours) in January 2023.
NJ: Can you share what Phase Two might look like?
GD: Phase Two will include the establishment of a laboratory so that traders from all over Ethiopia can have their goods graded and valued. Phase Three will include the creation of a cutting school, and Phase Four will see us establish a jewelry-making school. We are hopeful that all will be up and running by the end of 2023.
Ultimately, we want to create a sustainable model that can be implemented throughout Africa and that covers the entire supply chain. While our initial plans have targeted Ethiopia, Kenya, DRC, Nigeria, and Sierra Leone, we are already getting interest from other countries. I am hopeful they will come, see what we are achieving, and want to work with us to set up similar centers.
We need to build a solid foundation so that this initiative can endure and be operational far into the future. At the World Gem Foundation, we talk about training the next generation of gemologists, but here in Africa, there is not even a first generation of gemologists. This must change.
NJ: What can the industry do to help?
GD: As I mentioned earlier, funding is our biggest challenge. It would be wonderful if some of the big players in the industry got involved. I am tired of hearing words instead of actions. We all make a living from the gem industry, so I believe it is important that we do everything we can to support it and those engaged in it.
I know some will not be in favor of this initiative. They don’t want to change the current dynamic and will resist change, but I have always said there’s no downside to education. It is the greatest gift you can give a person. It empowers people and has the ability to transform lives. I truly hope that people will see the ‘bigger picture’ and embrace this initiative. Collectively, we can make a huge difference here in Africa, and I am determined that one way or another, we will succeed.
The Latest

Said to be the first to write a jewelry sales manual for the industry, Zell is remembered for his zest for life.

The company outfitted the Polaris Dawn spaceflight crew with watches that will later be auctioned off to benefit St. Jude’s.

A buyer paid more than $100,000 for the gemstone known as “Little Willie,” setting a new auction record for a Scottish freshwater pearl.

Supplier Spotlight Sponsored by GIA.

Anita Gumuchian created the 18-karat yellow gold necklace using 189 carats of colored gemstones she spent the last 40 years collecting.


The three-stone ring was designed by Shahla Karimi Jewelry and represents Cuoco, her fiancé Tom Pelphrey, and their child.

The Manhattan jewelry store has partnered with Xarissa B. of Jewel Boxing on a necklace capsule collection.

Supplier Spotlight Sponsored by GIA

Acting as temporary virtual Post-it notes, Notes are designed to help strengthen mutual connections, not reach new audiences.

The jewelry historian discusses the history and cultural significance of jewelry throughout time and across the globe.

From fringe and tassels to pieces that give the illusion they are in motion, jewelry with movement is trending.

The designer and maker found community around her Philadelphia studio and creative inspiration on the sidewalks below it.

The change to accepted payment methods for Google Ads might seem like an irritation but actually is an opportunity, Emmanuel Raheb writes.

The industry consultant’s new book focuses on what she learned as an athlete recovering from a broken back.

The fair will take place on the West Coast for the first time, hosted by Altana Fine Jewelry in Oakland, California.

Hillelson is a second-generation diamantaire and CEO of Owl Financial Group.

Submissions in the categories of Jewelry Design, Media Excellence, and Retail Excellence will be accepted through this Friday, Aug. 23.


Known as “Little Willie,” it’s the largest freshwater pearl found in recent history in Scotland and is notable for its shape and color.

Clements Jewelers in Madisonville cited competition from larger retailers and online sellers as the driving factor.

Most of the 18th century royal jewelry taken from the Green Vault Museum in Dresden, Germany, in 2019 went back on display this week.

The Pittsburgh jeweler has opened a store in the nearby Nemacolin resort.

With a 40-carat cabochon emerald, this necklace is as powerful and elegant as a cat.

The Erlanger, Kentucky-based company was recognized for its reliability when it comes to repairs and fast turnaround times.

Unable to pay its debts, the ruby and sapphire miner is looking to restructure and become a “competitive and attractive” company.

The trend forecaster’s latest guide has intel on upcoming trends in the jewelry market.

Ingraham said she’ll use the scholarship funds to attend the Women’s Leadership Program at the Yale School of Management.

Moijey Fine Jewelry & Diamonds held a three-week “Mine to Finger 3D Jewelry Program.”





























